Agricultural density, a concept that has garnered significant attention in recent years, refers to the measure of the quantity of agricultural production per unit area of land. This metric is crucial in understanding the efficiency and productivity of agricultural practices, as well as their impact on the environment and food security. As the global population continues to grow, the need to optimize agricultural density has become increasingly important. In this article, we will explore five ways agricultural density works, highlighting its significance, benefits, and challenges.
Key Points
- Agricultural density is a critical factor in determining the efficiency and productivity of agricultural practices.
- Increasing agricultural density can help meet the world's growing food demands while minimizing the environmental impact.
- There are various ways to improve agricultural density, including the use of high-yielding crop varieties, precision agriculture, and conservation agriculture.
- Agricultural density is closely linked to other important factors, such as water usage, soil health, and biodiversity.
- Striking a balance between agricultural density and environmental sustainability is essential for ensuring long-term food security.
Understanding Agricultural Density

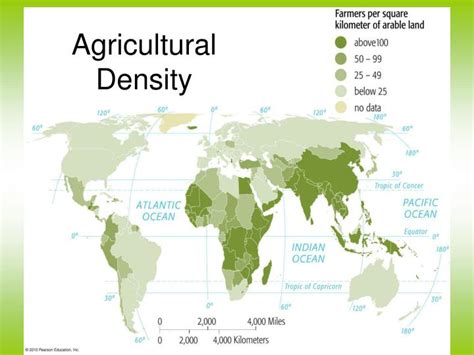
Agricultural density is often measured in terms of the amount of produce per hectare of land. This can include crops such as corn, wheat, and soybeans, as well as livestock such as cattle, pigs, and chickens. The density of agricultural production can vary significantly depending on factors such as climate, soil quality, and farming practices. For example, countries with high levels of agricultural density, such as the Netherlands and Singapore, are able to produce a large quantity of food per unit area of land, while countries with lower levels of agricultural density, such as those in sub-Saharan Africa, may struggle to meet the food needs of their populations.
Factors Influencing Agricultural Density
Several factors can influence agricultural density, including the type of crop or livestock being produced, the level of technology and infrastructure available, and the presence of pests and diseases. Additionally, factors such as climate change, soil degradation, and water scarcity can all impact agricultural density. For instance, a study by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) found that climate change is projected to reduce agricultural productivity by up to 2% per decade, resulting in decreased agricultural density and food security.
| Factor | Influence on Agricultural Density |
|---|---|
| Crop Type | High-yielding crop varieties can increase agricultural density |
| Technology and Infrastructure | Advanced technology and infrastructure can improve agricultural efficiency and increase density |
| Pests and Diseases | Pests and diseases can reduce agricultural density by decreasing crop yields |
| Climate Change | Climate change can reduce agricultural density by altering growing conditions and increasing weather-related stresses |

Methods for Improving Agricultural Density

There are several methods that can be used to improve agricultural density, including the use of high-yielding crop varieties, precision agriculture, and conservation agriculture. High-yielding crop varieties are bred to produce more per unit area of land, while precision agriculture involves the use of advanced technology, such as drones and satellite imaging, to optimize crop growth and reduce waste. Conservation agriculture, on the other hand, involves the use of practices such as no-till or reduced-till farming, cover cropping, and crop rotation to promote soil health and reduce erosion.
Benefits of Increased Agricultural Density
Increasing agricultural density can have several benefits, including increased food production, reduced environmental impact, and improved economic viability. By producing more food per unit area of land, farmers can help meet the world’s growing food demands while minimizing the need for deforestation and habitat destruction. Additionally, increased agricultural density can help reduce the environmental impact of farming by reducing the amount of land needed for production, conserving water, and promoting more efficient use of resources.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the benefits of increased agricultural density, there are also several challenges and limitations to consider. One of the main challenges is the potential for decreased biodiversity, as high-yielding crop varieties and precision agriculture can lead to a reduction in crop diversity. Additionally, the use of advanced technology and infrastructure can be expensive, making it inaccessible to small-scale farmers in developing countries. Furthermore, increased agricultural density can also lead to increased water usage, soil degradation, and pollution, highlighting the need for sustainable and environmentally friendly practices.
What is agricultural density, and why is it important?
+Agricultural density refers to the measure of the quantity of agricultural production per unit area of land. It's essential for understanding the efficiency and productivity of agricultural practices, as well as their impact on the environment and food security.
How can agricultural density be improved?
+Agricultural density can be improved through the use of high-yielding crop varieties, precision agriculture, and conservation agriculture. Additionally, practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and integrated pest management can help promote soil health and reduce erosion.
What are the benefits of increased agricultural density?
+The benefits of increased agricultural density include increased food production, reduced environmental impact, and improved economic viability. By producing more food per unit area of land, farmers can help meet the world's growing food demands while minimizing the need for deforestation and habitat destruction.
In conclusion, agricultural density is a critical factor in determining the efficiency and productivity of agricultural practices. By understanding the factors that influence agricultural density and adopting methods to improve it, farmers and policymakers can help ensure global food security while minimizing the environmental impact of farming. As the world’s population continues to grow, the need to optimize agricultural density will become increasingly important, highlighting the need for sustainable and environmentally friendly practices that promote soil health, conserve water, and reduce waste.